Export data#
Once we’ve computed signals and concepts over a dataset, it can be very useful to download the results so downstream applications can used the enrichments.
From the UI#
We can download the results by clicking the Download icon in the top-right of the dataset view:
![]()
This will open a modal which lets you choose fields to download, with a preview of the download results:
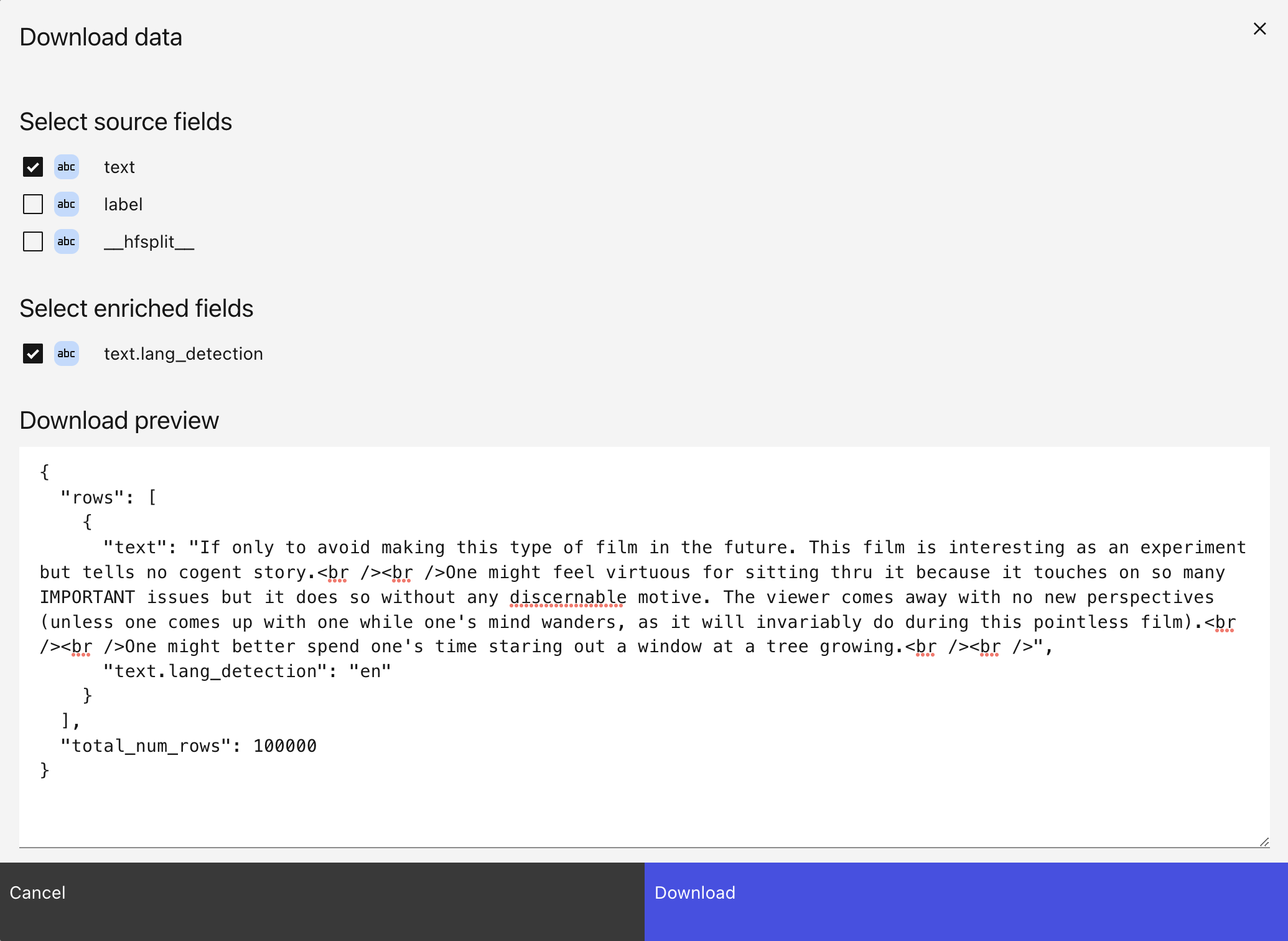
Click “Download” to download the results as a JSON file from the browser.
From Python#
In Python, we can export to different formats using the Dataset.to_pandas,
Dataset.to_json, Dataset.to_parquet, Dataset.to_csv and Dataset.to_huggingface
methods.
Let’s export the text and text.language_detection to a pandas dataframe:
dataset = ll.get_dataset('local', 'imdb')
# NOTE: you can also select lang detection with ('text', 'language_detection')
df = dataset.to_pandas(columns=['text', 'text.lang_detection'])
print(df)
Let’s export all the columns to a JSONL file:
dataset.to_json('imdb.jsonl', jsonl=True)
Labels#
If you have manually labeled some of the rows, you can choose to only export rows that include a certain label:
dataset.to_json('imdb.jsonl', jsonl=True, include_labels=['good_data'])
or rows that exclude a certain label:
dataset.to_json('imdb.jsonl', jsonl=True, exclude_labels=['bad_data'])
Filtering#
We can also filter the rows we export. The filter API is the same as in
Dataset.select_rows. For example, let’s only export rows where the
language is en:
dataset.to_json('imdb.jsonl', jsonl=True, filters=[('text.lang_detection', 'equals', 'en')])
or where the toxicity is < 0.3:
dataset.to_json('imdb.jsonl', jsonl=True, filters=[('text.lilac/toxicity/gte-small.score', 'less', 0.3)])