Deploying on HuggingFace spaces#
Lilac projects can be deployed to HuggingFace spaces out of the box.
You can either use our Deployer UI, our Python API / CLI, or Duplicate our public space.
Option 1: Use the Lilac Deployer UI 🚀#
There are two pages in the deployer UI.
Select your HuggingFace dataset to read, config, splits, and read tokens.
Select your HuggingFace space to write to. You will need a HuggingFace write token which you can get from your HuggingFace settings.
This will create a HuggingFace space, reading your HuggingFace dataset upon bootup.
Option 2: Deploy from Python / CLI#
This requires:
You to be logged in with HuggingFace with
huggingface-cli login.Have the
huggingface_hubpip package installed.
Python#
The accompanying IPython notebook can be found here.
Deploy a project#
To deploy a project directory that you’ve loaded locally, you can use the lilac.deploy_project
method. For more information on Lilac projects, see Lilac Projects.
ll.deploy_project(
hf_space='my_hf_org/my_hf_space',
project_dir='~/my_project',
create_space=True # Create the HuggingFace space if it doesn't exist.
)
This will upload all datasets, concepts, model caches. Locally run datasets will be uploaded to HuggingFace datasets with signals, concepts, embeddings uploaded. These will be downloaded when the space boots up.
See the Reference for more options for deploy_project.
Deploy a Config#
If you just want to deploy a config, and not run anything locally, you can use deploy_config.
This will push the config to HuggingFace spaces and will load all the data when the server boots up
on HuggingFace.
NOTE: Embeddings, signals, concepts will be computed on HuggingFace, which could be expensive.
Deploy the glue HuggingFace dataset with config=ax to
HuggingFace, and load the dataset in the space.
ll.deploy_config(
hf_space='my_hf_org/my_hf_space',
create_space=True,
config=ll.Config(datasets=[
ll.DatasetConfig(
namespace='local',
name='glue_ax',
source=ll.HuggingFaceSource(dataset_name='glue', config_name='ax'))
]))
CLI#
You can also deploy a project directly from the CLI:
lilac deploy-project \
--hf_space=my_hf_org/my_hf_space \
--create_space
--project_dir=~/my_project
This will deploy all datasets, concepts, and caches from your project to the HuggingFace space.
If you only want to deploy a subset of datasets, you can pass:
--dataset local/dataset1 --dataset local/dataset2
If you only want to deploy a subset of concepts, you can pass:
--concept local/concept1 --concept local/concept1
Option 3: Duplicate the HuggingFace demo#
Lilac hosts a HuggingFace spaces demo so you can try Lilac before installing it.
Thanks to HuggingFace, this space can be duplicated and customized with your own data. You can decide to make your duplicated private for use with private or sensitive data.
To duplicate the space, click the hamburger menu in the top-right of the space and click Duplicate this Space:
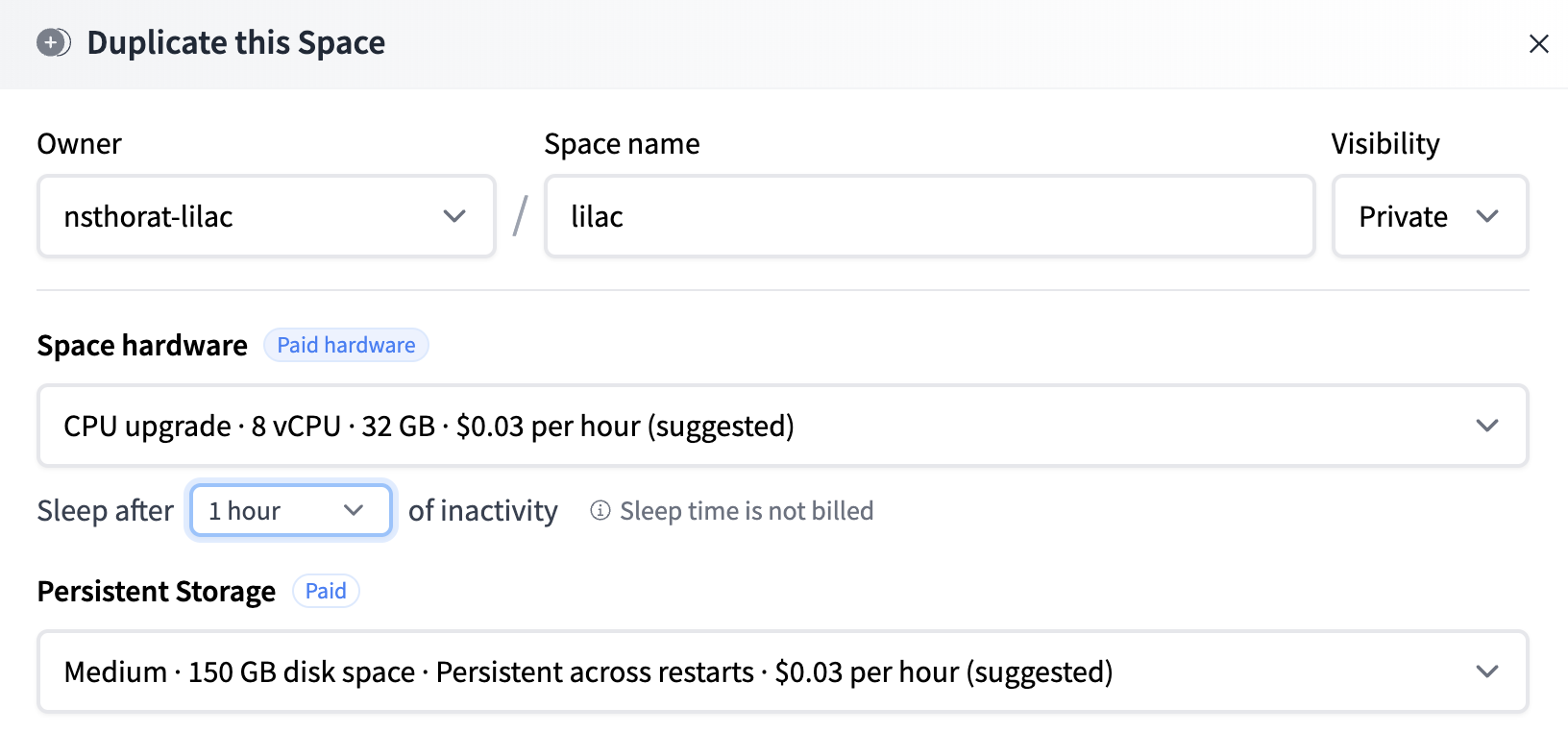
This will open a modal which allows to to determine the machine. We recommend using persistent storage as it will allow you to save results of computations permanently (loading datasets, making concepts, computing signals and concepts). However, if you decide not to pay for persistent storage, you can still use Lilac, but results of computations will lost when the image reboots.
The modal also contains options for environment variables.
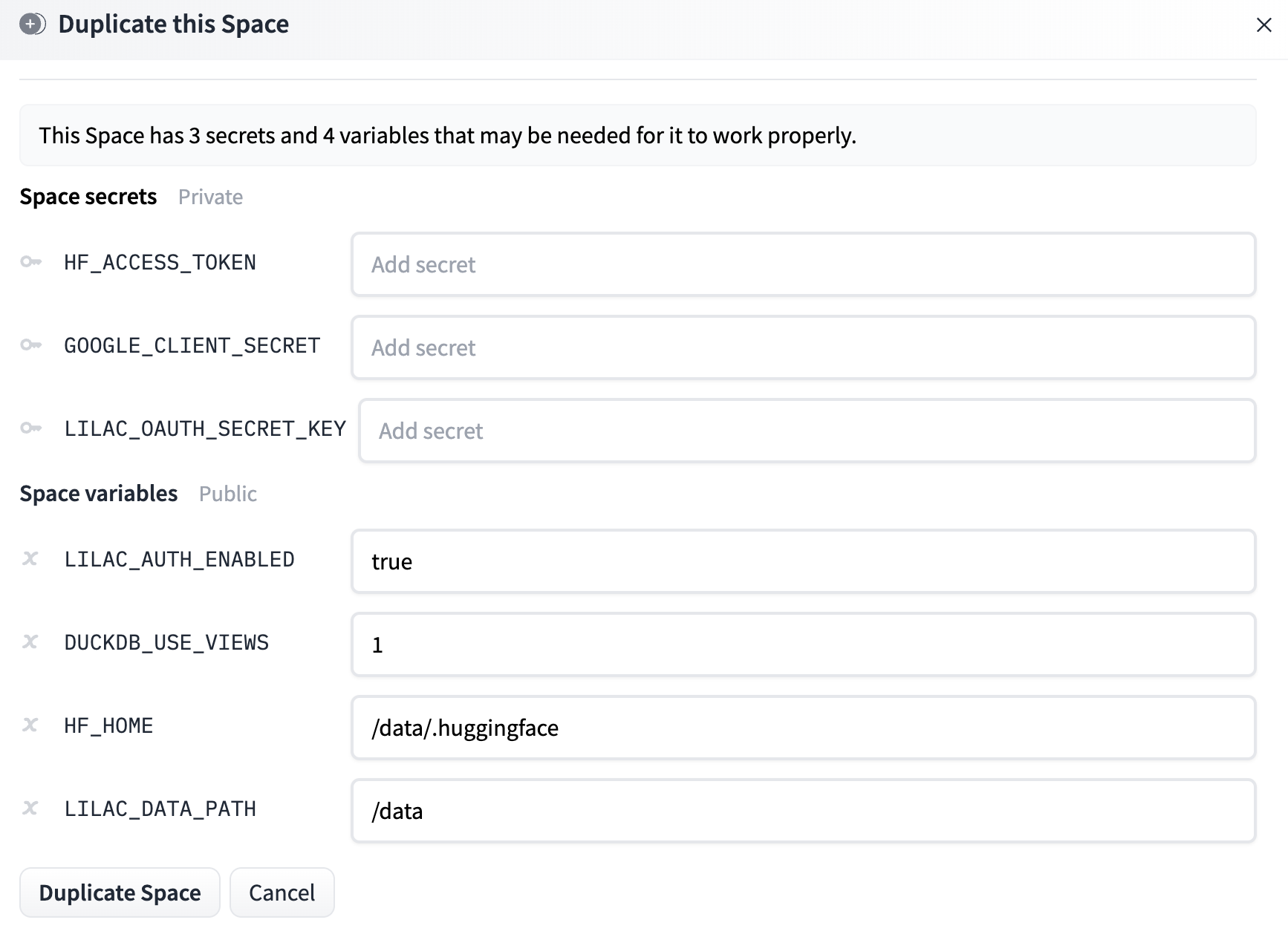
Secrets:
HF_ACCESS_TOKEN: If your space is private or reads from private data hosted on HuggingFace, set this to a HuggingFace access token with read permissions, allowing the space to download the datasets upon boot. See HuggingFace User access tokens for more details.GOOGLE_CLIENT_SECRET: If you wish to enable authentication on your server, define this variable to be the client secret of a Google Application you create. You should also defineGOOGLE_CLIENT_ID. Details can be found at Using Oauth 2.0 to Access Google APIs.LILAC_OAUTH_SECRET_KEY: If you wish to enable authentication on your server, this should be defined as a random string. Details in the Oauth link above.
Space variables:
LILAC_AUTH_ENABLED: Whether to enable Google authentication on your duplicated server. Set this tofalse, or delete it, to disable Google authentication. If your HuggingFace space is private, you can set this tofalseand rely on HuggingFace space authentication.HF_HOME: This should be kept/data/.huggingfaceif you plan on using Persistent Storage. This allows the HuggingFace cache to be persistent. If you are not, you should remove this variable entirely.LILAC_PROJECT_DIR: The path where data for datasets, concept models and Lilac caches are stored. This should be kept/dataif you plan on using Persistent Storage. If you are not, this should be set to the relative path./datawhich lives ephemerally in the docker image. It is important to use./databecause it has been given writen permissions by the docker image. See HuggingFace Disk usage on Spaces for documentation on Persistent Storage.LILAC_DATA_PATH: Deprecated in favor ofLILAC_PROJECT_DIR.GOOGLE_ANALYTICS_ENABLED: Set this to “false” to disable our Google Analytics tracking on the HuggingFace demo. We use this just to track basic session information on the public demo.
After you click the duplicate space button, the space will be duplicated and start building the docker image in your own space.
Once the image is built, your space is now running a personalized Lilac instance!
For more details on environment variables, see Environment Variables.
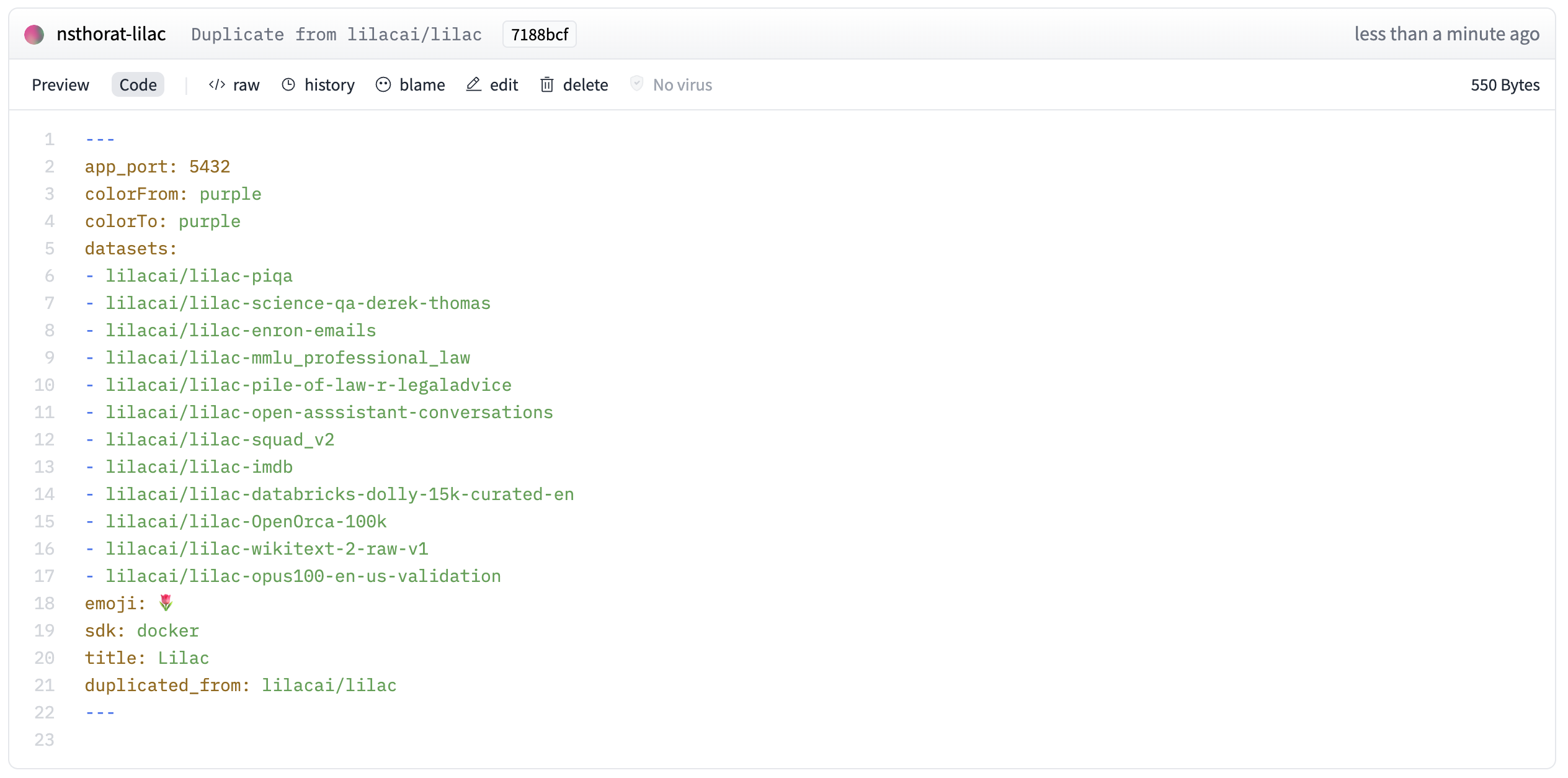
Removing datasets#
You’ll notice that the demo will try to load the same datasets from the lilacai/lilac space. This may lead to an out of memory error when cloning locally.
To remove these, edit the README.md on the space and delete the datasets under the linked
datasets field for the HuggingFace space configuration. The space will restart.
If these datasets were synced in the process, you can delete them from the UI.